Study Details
Study Title: Accident Effects of Sideslope and Other Roadside Features on Two-Lane Roads
Authors: Zegeer et al.
Publication Date: 1988
Abstract: The purposes of this study were to (1) develop one or more methods for quantifying roadside hazard, (2) define factors that influence run-off-road accidents, and (3) estimate the accident benefits of various roadside improvements. Detailed traffic, accident, roadway, and roadside data were collected on 4,951 miles of two-lane rural roads in seven states. Roadside data included development and use of a pictorial seven-point roadside hazard scale, a measure of roadside recovery (clear zone) distance, field sideslope measurements, and detailed types of and lateral distances to roadside obstacles. Statistical testing was used along with log-linear modeling to determine the interactive effects of roadside and roadway features on accidents. Flatter sideslopes of 3:1 to 7:1 were found to be related to lower rates of single-vehicle accidents. However, only a 2 percent reduction in single-vehicle accidents was found for a 3:1 sideslope compared to a 2:1 sideslope. Reductions in related accidents due to general roadside improvements were found to range from 19 percent to 52 percent, depending on the amount of roadside improvement. Trees and utility poles are the roadside objects most often struck. Obstacles associated with the highest percent of severe accidents include culverts, trees, utility and light poles, bridges, rocks, and earth embankments.
Study Citation: Zegeer, C.V., D.W. Reinfurt, W.W. Hunter, J. Hummer, R. Stewart, and L. Herf. Accident Effects of Sideslope and Other Roadside Features on Two-Lane Roads. In Transportation Research Record 1195. TRB, National Research Council, Washington, DC, 1988, pp. 33-47
Study Report: Download the Study Report Document
CMFs Associated With This Study
Category: Roadway
Countermeasure: Convert 12-foot lanes to 10-foot lanes
| CMF | CRF(%) | Quality | Crash Type | Crash Severity | Roadway Type | Area Type |
|---|
| 1.02 | -2 | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
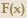 | | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
| 1.23 | -23 | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
| 1.01 | -1 | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
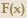 | | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
| 1.15 | -15 | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
Countermeasure: Convert 12-foot lanes to 11-foot lanes
| CMF | CRF(%) | Quality | Crash Type | Crash Severity | Roadway Type | Area Type |
|---|
| 1.01 | -1 | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
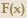 | | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
| 1.04 | -4 | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
| 1.01 | -1 | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
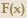 | | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
| 1.03 | -3 | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
Countermeasure: Convert 12-foot lanes to 9-foot or less
| CMF | CRF(%) | Quality | Crash Type | Crash Severity | Roadway Type | Area Type |
|---|
| 1.04 | -4 | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
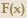 | | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
| 1.38 | -38 | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
| 1.03 | -3 | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
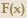 | | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |
| 1.25 | -25 | text text | Head on,Run off road,Sideswipe,Single vehicle | All | Principal Arterial Other | Rural |

